Which Type Of Vaccines Triggers The Recipient’s Immune System To Produce Antitoxins?
Which type of vaccines triggers the recipient's immune system to produce antitoxins?. These specific antibodies will remain in the immune system after the infection has gone. These antibodies act as scouts hunting down the infectious agent and marking it for destruction by the immune system. TLR4 signalling can trigger the activation and recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages that can kill or limit the spread of infection at an early stage allowing time for the adaptive immune response to develop.
Types of Antibody Reactions Upon exposure to an antigen specific. Vaccination protects people from natural infection mainly by stimulating the humoral immune response and establishing immunological memory against a specific pathogen. Create vaccine from specific purified immunogenic macromolecules Examples.
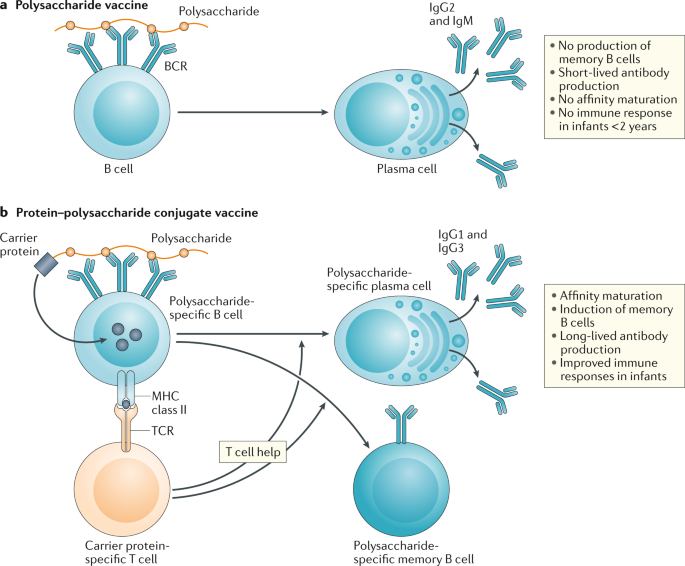
Conjugate subunit vaccines eg Haemophilus influenzae. Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity. Meningococcal meningitis vaccine Pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine Limitations Polysaccharide vaccines activate B cells in thymus-independent manner so that T H cells are not activated.
Passive immunization means administering antibodies or antitoxins from another source. Each type of vaccine is used for different diseases and different purposes. The type of adjuvant used determines the direction and type of immune system induced.
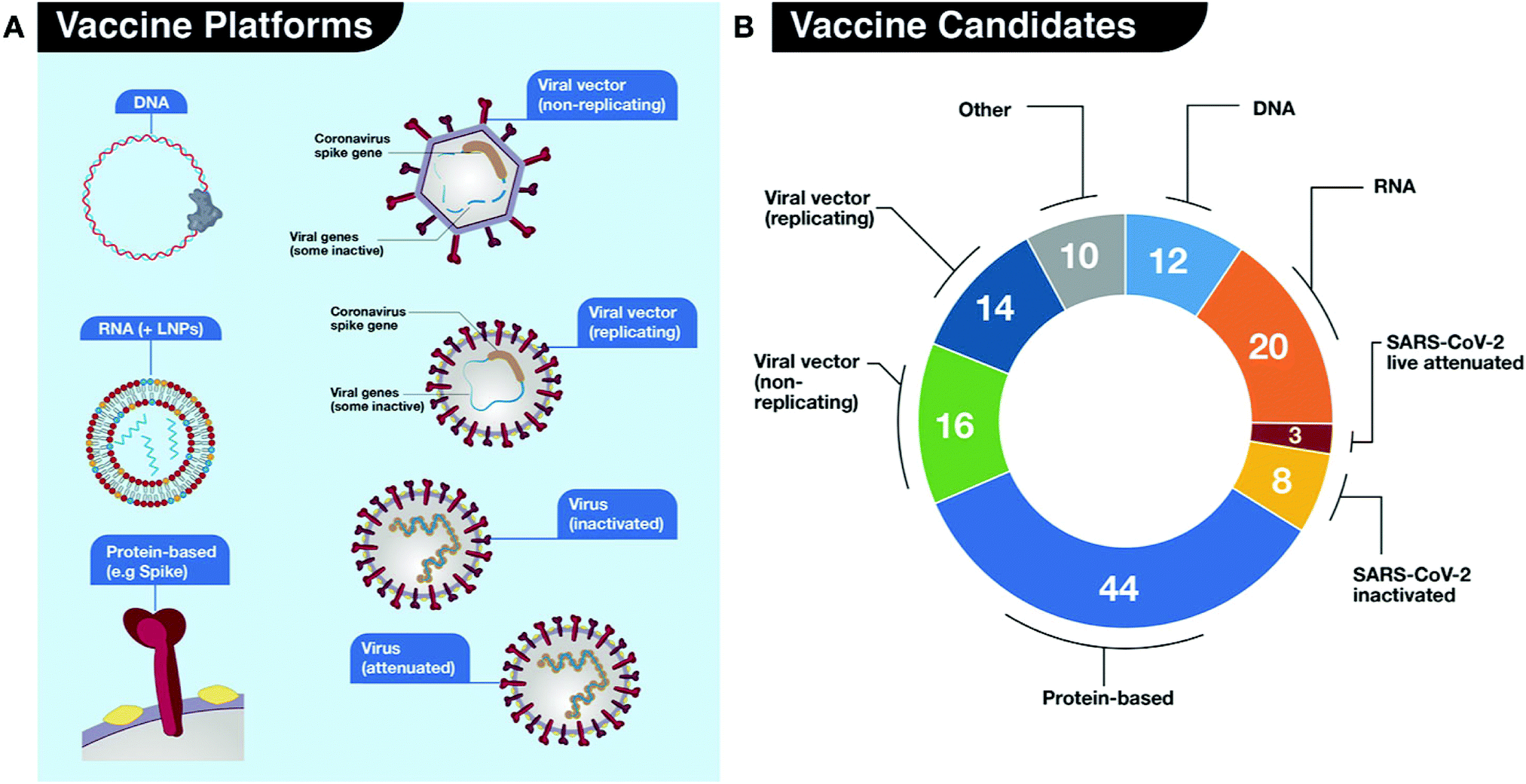
Newer vaccines contain the blueprint for producing antigens rather than the antigen itself. Each antibody is specific to the bacteria or virus that it has detected and will trigger a specific immune response. When given alive the organisms are weakened or attenuated by some laboratory means so that they still stimulate antibodies but do not.
There are two types of immunity. Most MLV vaccines do not contain adjuvants although there are exceptions. Examples of toxoids include diphtheria toxoid and tetanus toxoid and are discussed below.
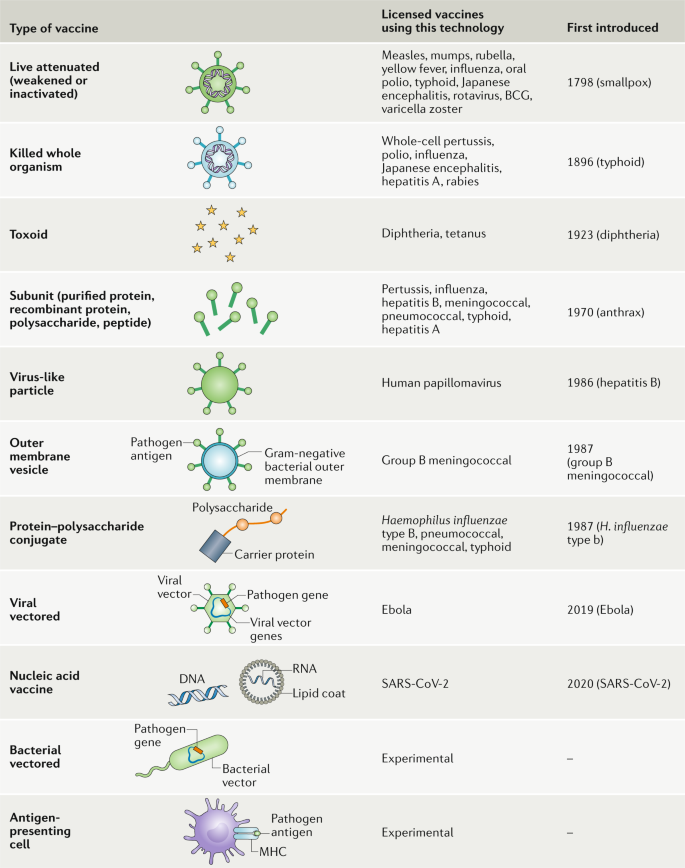
Type b and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines are produced. Today there are seven different types of commonly used vaccines.
Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity.
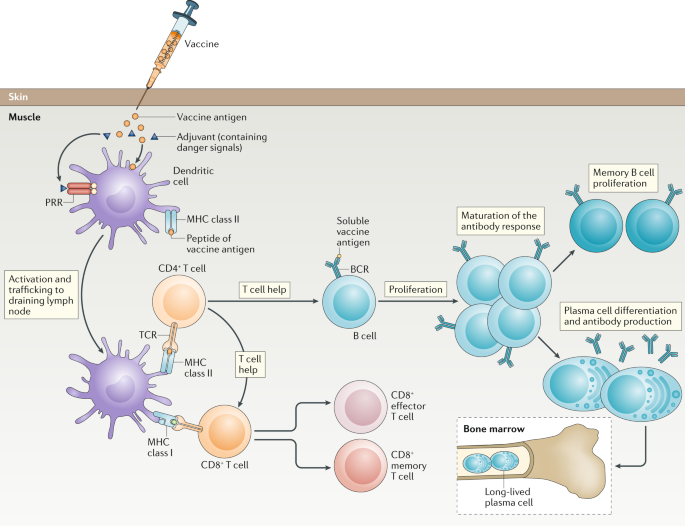
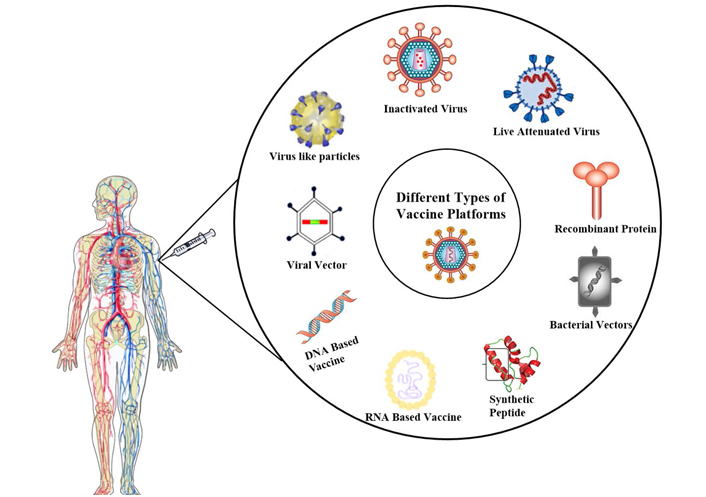
Passive immunization means administering antibodies or antitoxins from another source. Infection-causing microbes and the vaccines designed to combat them have portions of proteins called antigens. Infectious disease - Infectious disease - Immunization. The Role of Adjuvants As a rule adjuvants oil or water-based compounds are added to vaccines containing killed pathogens to boost the immune response. Epitope it marks it for attack destruction by the appropriate cells associated components of the immune system complement PMNs etc 1. Conjugate subunit vaccines eg Haemophilus influenzae. Receipt of hepatitis B vaccine is an example of active immunization. Produce IgM little IgG and limited if any immune memory. These vaccines are live inactivated subunit toxoid conjugate DNA or recombinant vector vaccines.
Receipt of hepatitis B vaccine is an example of active immunization. Examples of toxoids include diphtheria toxoid and tetanus toxoid and are discussed below. TLR4 signalling can trigger the activation and recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages that can kill or limit the spread of infection at an early stage allowing time for the adaptive immune response to develop. Most MLV vaccines do not contain adjuvants although there are exceptions. Create vaccine from specific purified immunogenic macromolecules Examples. An immune response begins when macrophages ingest antigens such as proteins entering the body and digest them into antigen. Antibodies floods through the hosts body fluids and wherever it binds to its.


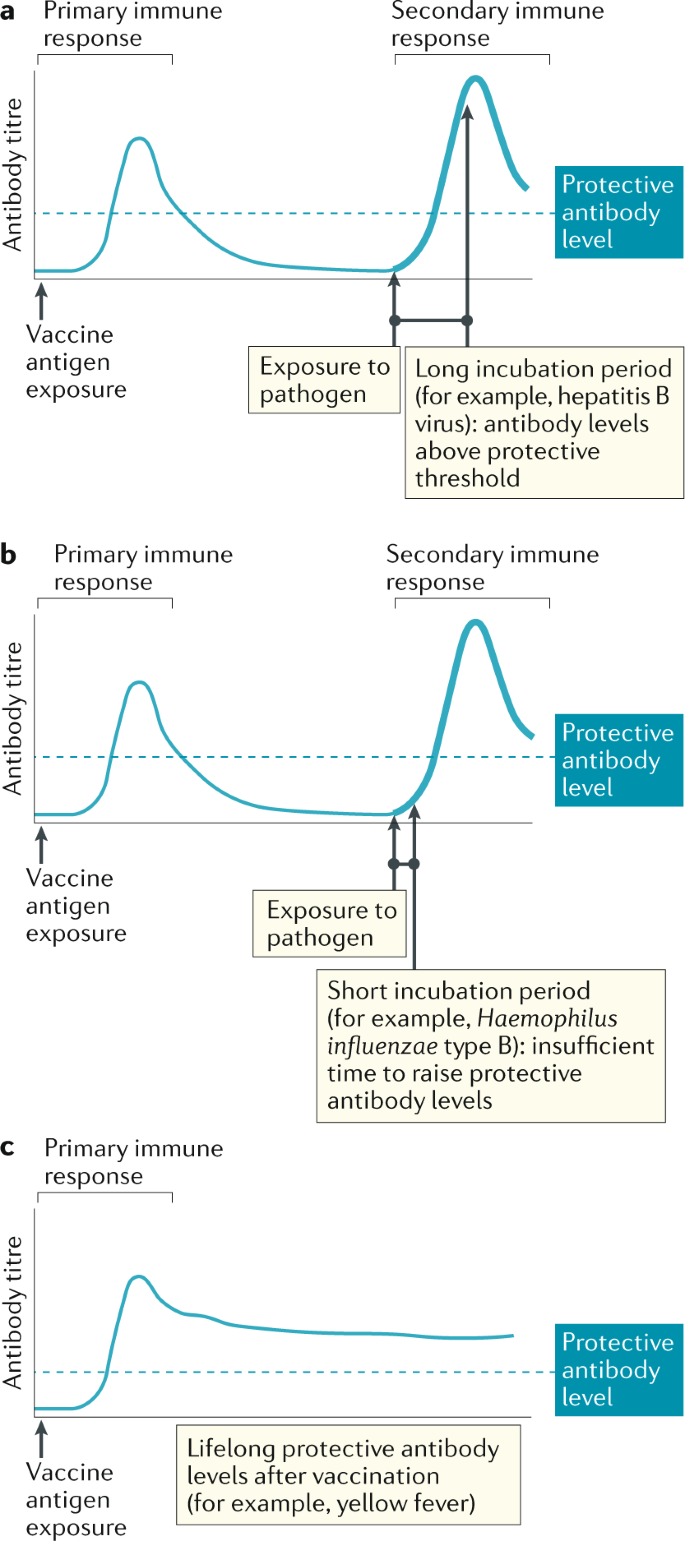
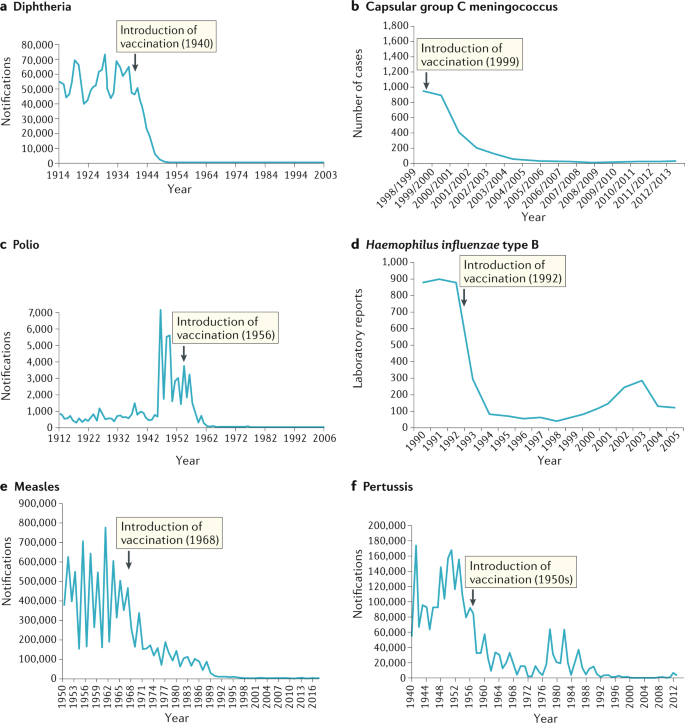
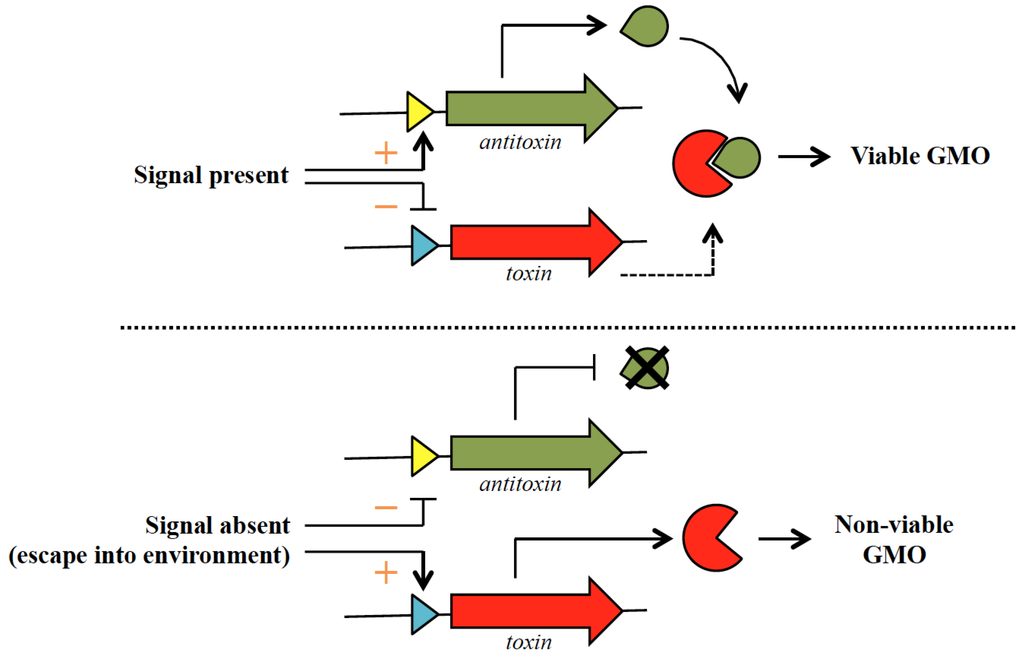

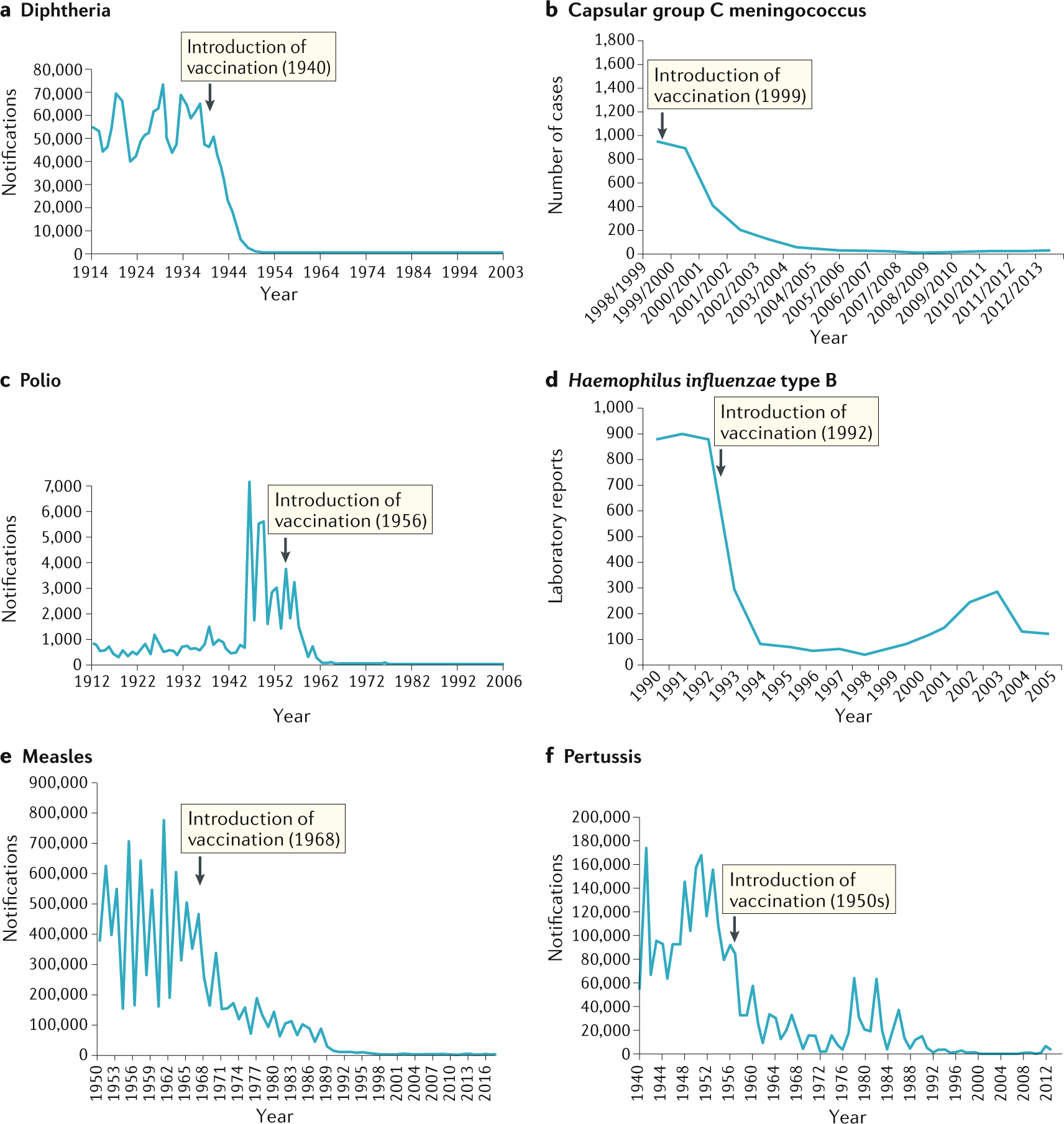











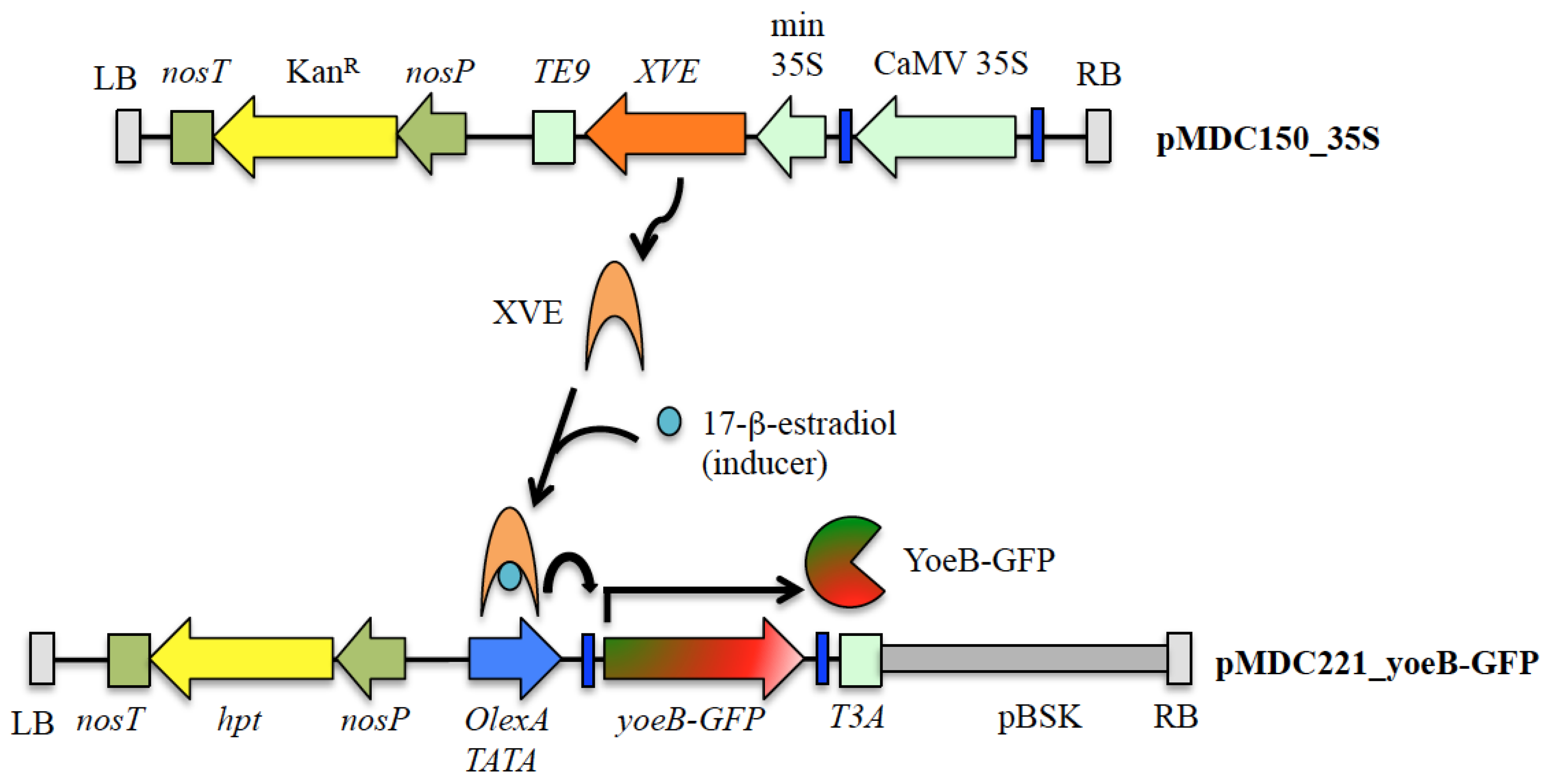
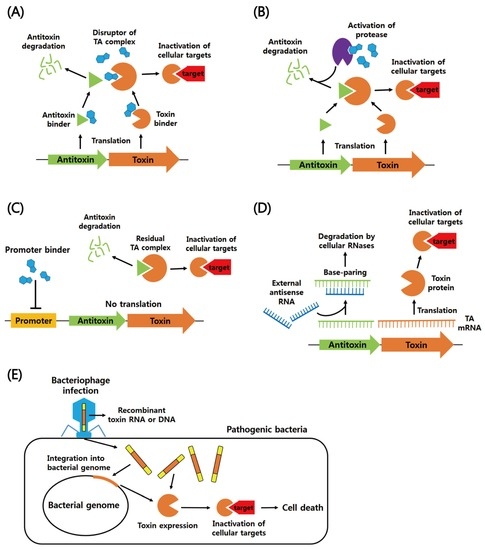
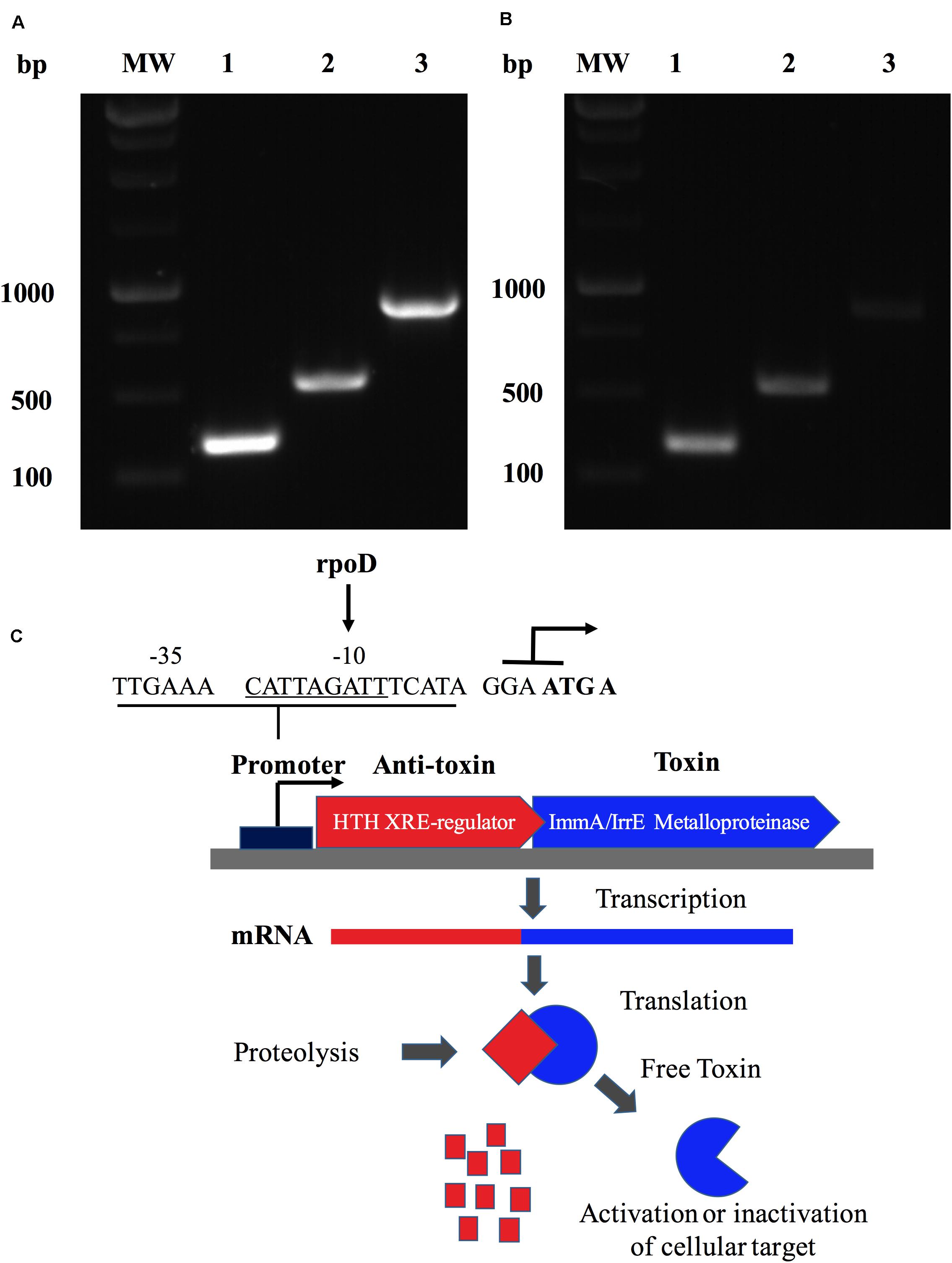


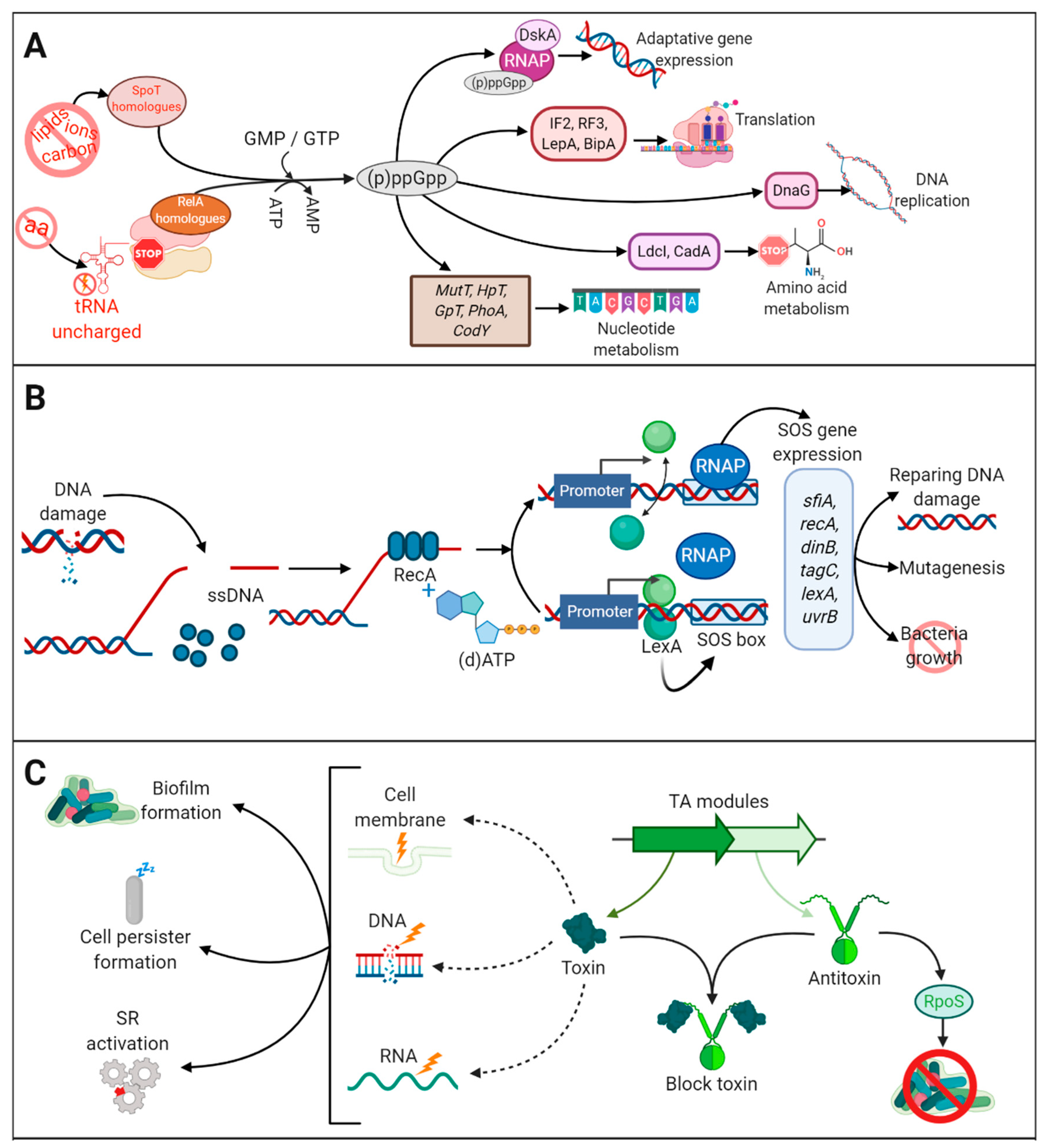








Post a Comment for "Which Type Of Vaccines Triggers The Recipient’s Immune System To Produce Antitoxins?"